ULTRA - A Foundation Model for KG Reasoning
Abstract
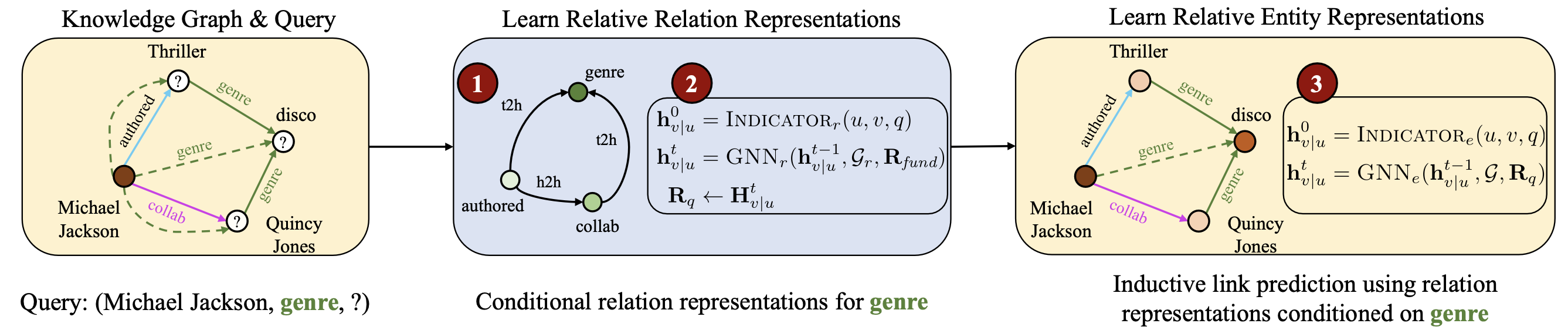
Foundation models in language and vision have the ability to run inference on any textual and visual inputs thanks to the transferable representations such as a vocabulary of tokens in language. Knowledge graphs (KGs) have different entity and relation vocabularies that generally do not overlap. The key challenge of designing foundation models on KGs is to learn such transferable representations that enable inference on any graph with arbitrary entity and relation vocabularies. In this work, we make a step towards such foundation models and present ULTRA, an approach for learning universal and transferable graph representations. ULTRA builds relational representations as a function conditioned on their interactions. Such a conditioning strategy allows a pre-trained ULTRA model to inductively generalize to any unseen KG with any relation vocabulary and to be fine-tuned on any graph. Conducting link prediction experiments on 57 different KGs, we find that the zero-shot inductive inference performance of a single pre-trained ULTRA model on unseen graphs of various sizes is often on par or better than strong baselines trained on specific graphs. Fine-tuning further boosts the performance.
Performance
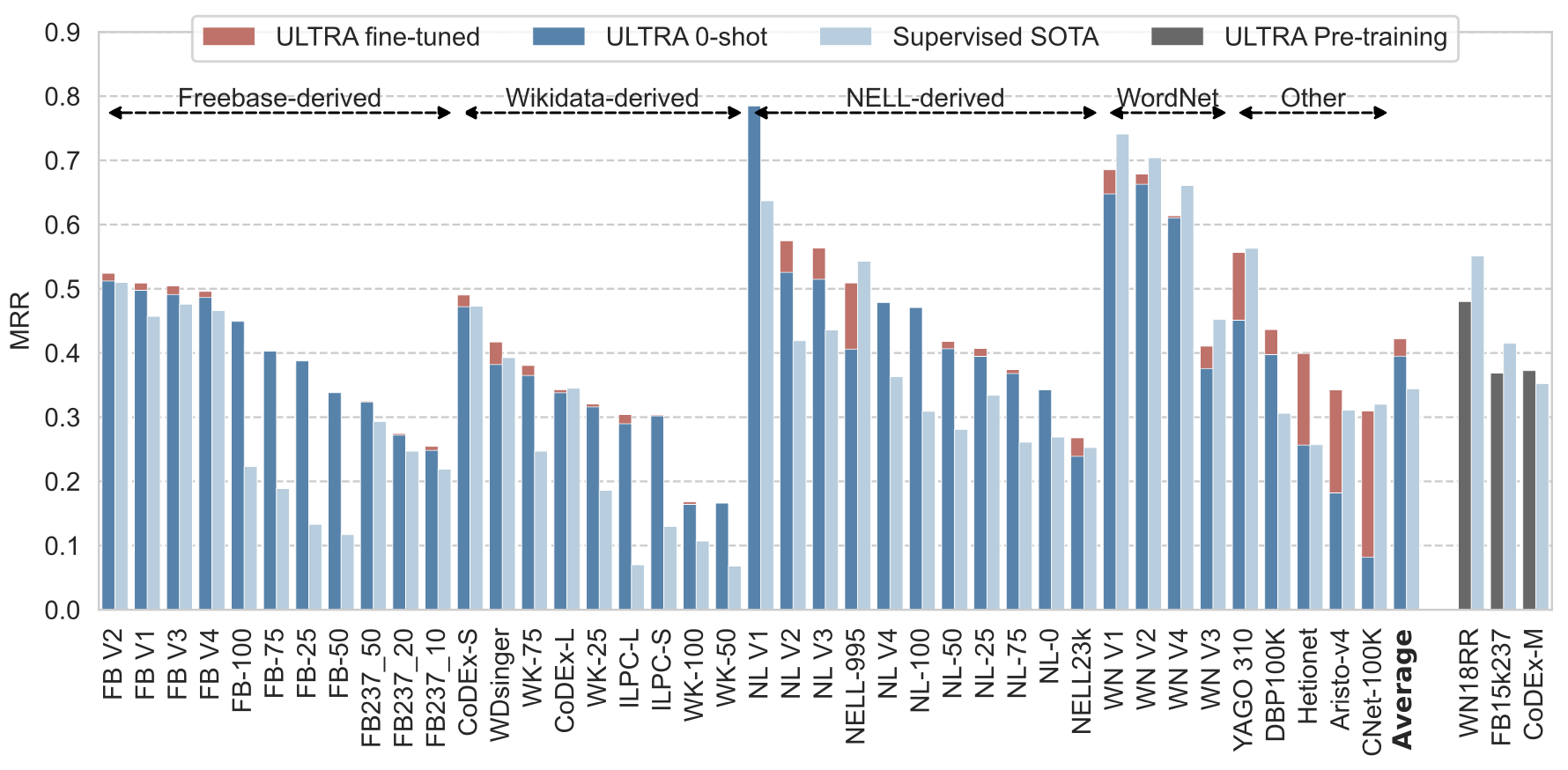
A single ULTRA model pre-trained on 3 standard KGs (FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium) outperforms supervised SOTA methods by relative 15% in terms of MRR and Hits@10 on 57 different KGs in the zero-shot regime, that is, seeing the new graphs at inference without any fine-tuning. Fine-tuning ULTRA brings further improvements and the overall gap increases to 22%.
Results on 51 KGs that have published baselines. 40 graphs were evaluated on the full-graph ranking. The last column compares to the baselines where metrics were computed against 50 random negatives due to computational complexity of the baselines. We also report full-graph metrics on those datasets in the paper. Pre-training performance of ULTRA is put into the fine-tuned category by convention.
| Model | Inductive datasets (27), MRR | Transductive datasets (13), MRR | Total Avg (40), MRR | Pretraining (3), MRR | Inductive (8), Hits@10 (50 negatives) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised SOTA | 0.342 | 0.348 | 0.344 | 0.439 | 0.731 |
| ULTRA 0-shot | 0.435 | 0.312 | 0.395 | - | 0.859 |
| ULTRA fine-tuned | 0.443 | 0.379 | 0.422 | 0.407 | 0.896 |
Scaling and Model Options
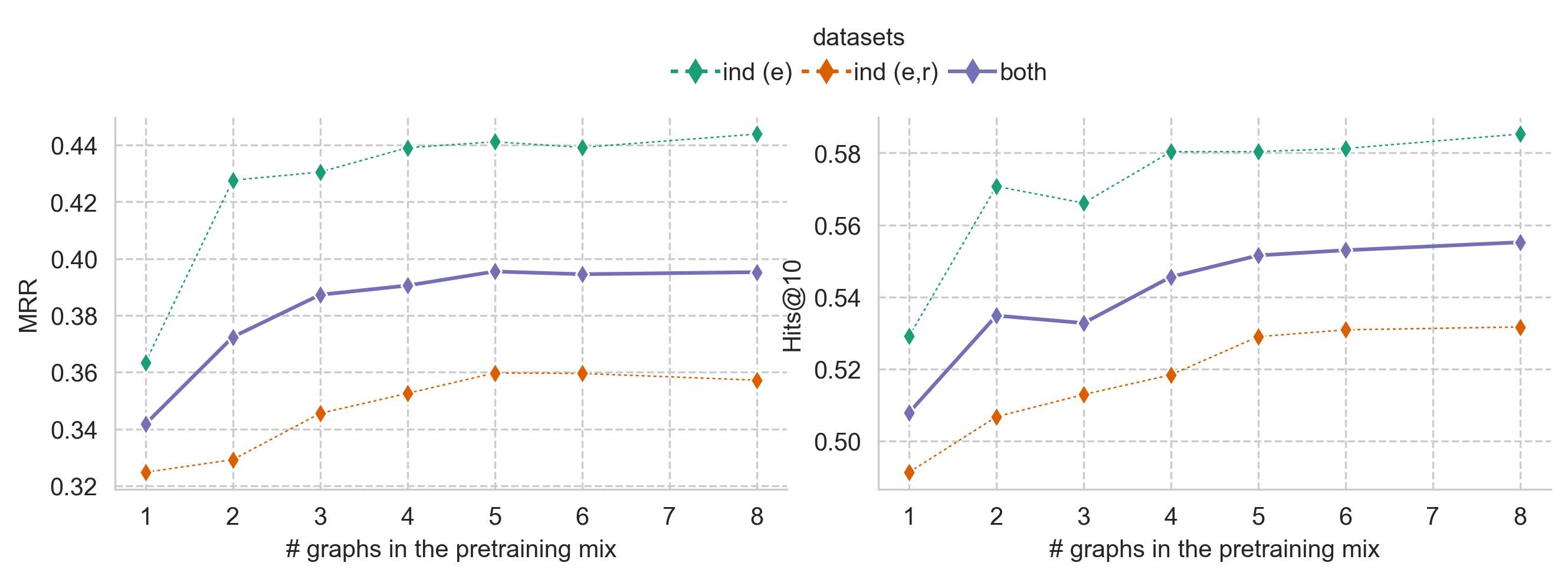
We trained several variants of the 177k parameter ULTRA model on different mixtures of KGs in the pre-training set.
- 1 graph: FB15k237 only
- 2 graphs: FB15k237, WN18RR
- 3 graphs (default): FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium
- 4 graphs: FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium, NELL-995
- 5 graphs: FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium, NELL-995, YAGO310
- 6 graphs: FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium, NELL-995, YAGO310, ConceptNet100k
- 8 graphs: FB15k237, WN18RR, Codex-Medium, NELL-995, YAGO310, ConceptNet100k, DBpedia100k, AristoV4
The checkpoints are rather small (a few MB), the weights and code are now available.